While you may view search engines as a neutral tool for querying, in actuality, search engines are created by company-affiliated individuals and operate much like any product. They’re designed to satisfy the consumer and financially benefit the producer.
Although this realistic view of search engine intent shouldn’t necessarily raise any red flags, what might concern you is how search engines serve up results.
Google, in particular, intervenes algorithmically to remove spam results that the search engine believes are useless to the consumer. While it is arguable that less spam is a good and welcome thing, what happens if Google deems your site spam?
In addition to the removal of spam, Google is a habitual booster of massive corporations such as Amazon and Facebook. The rationale for boosting larger sites is not particularly nuanced.
Big names can outperform small companies when it comes to SEO, and they typically offer a wider selection of items that can satisfy the consumer. With that said, this Google bias can underserve your site by burying it under offerings from big names.
In the world of Google bias, you need to understand how the deck is stacked against small businesses and actively work to ensure your site performs to the best of its ability.
How Are Search Engines Biased?
When you encounter the word “bias,” you might associate it with nefarious connotations.
Although there have been claims that Google bias slants search results against particular political leanings, when it comes to search engines, Google bias overall tends to trend more toward erring too heavily on the perceived wants of their audience.
Google search algorithms are based on a slew of information, including the phrasing of your query, the reliability of sources, the relevance of pages, and countless other factors. Even your location and settings can help Google discover the most relevant information for your search.
It stands to reason that the aggregation of this information lends itself toward suggesting sources that try to match and satisfy past behavior, as well as other defining indicators.
In addition to these algorithms, Google bias can be impacted by domain authority (DA), a ranking metric that indicates both your site’s success in ranking on search engines, as well as your site’s perceived expertise surrounding a specific topic.
DA is measured by various factors, including inbound links, which are vitally important to score calculation. With an increased amount of inbound links from other relevant domains comes an increased DA score, in most cases.
The Effect of Search Engine Bias on Businesses
Unfortunately, bias (whether helpful or not) can significantly impact small businesses that have few inbound links and sparse content. For big organizations with equally big wallets, constant content creation can earn inbound links and score a high DA score, helping them land top positions on search engine results pages (SERPs).
Collectively, the above factors can severely limit your site’s search result visibility. Not only are you competing against big brand names, but you’re also losing SERP traction if you’re not actively recruiting inbound links and establishing expertise.
There is also a chance your DA will decrease when a massively popular site (think Twitter) gains a large number of inbound links, deflating your search rank and lowering your overall DA score.
For sites as large as Twitter or Amazon, there’s not much a small business can do to compete with the sheer number of inbound links and resulting high DA. However, you can aim to earn a higher score than your competitors by employing white hat strategies to combat Google bias.
Ethical Strategies for Combating Search Engine Biases
While the above may seem daunting for small-to-medium business owners looking to grab some top-SERP terrain, you can use several strategies to help you compete for those rankings.
By incorporating the following four approaches into your digital strategy, you can compete in the battle for search visibility.
Focus on a Single Subject
While it’s clear that Google bias means delivering results from big-name sites, the algorithm is also partial to sites that focus on a single subject in depth.
This strategy not only helps you earn points in Google’s algorithm, but it also helps you establish yourself as an industry expert in your field.
Instead of creating a range of content, focus on a single topic that satisfies every component of the buyer’s journey and build out a content map from there.
This task might seem overwhelming due to the sheer amount of potential content, so here are three places to start:
- Content that educates on early-journey topics
- Content that highlights your point of view on your topic
- Content that explains industry perspectives on the topic
Build Site Relevance
When we talk about search engines, the word “relevance” references how much a site’s content correlates to the active search term.
Much like DA, relevance is vitally important in determining where your site lands on the SERPs for a specific query.
To improve your site relevance score, you should determine intent around user search and create a content strategy to match those queries.
Also, make sure you are relevant to user queries by having the most up-to-date business information on your site and local search profiles.
Earn Inbound Links
Inbound links (or backlinks) are links coming to your site from an external source. This type of link does a great amount of work to improve your site’s perceived expertise. If another site is linking to your content as a point of clarification or for additional information, you’re clearly an expert in the field.
While this all sounds wonderful, how do you earn those inbound links? With many strategies available for the savvy marketer, below are our top five white hat steps for success that can help you grow your number of inbound links and reduce Google bias.
Score Inbound Links
When you write good content, good things may happen.
Editorial inbound links are the holy grail of link building: they’re free and they’re lasting.
Next time you’re crafting content, consider the true value of the piece and assess how your audience will use it.
If it’s helpful to your industry and includes a how-to, chances are it can earn you at least one inbound editorial link. It’s just because you wrote great content.
Craft Useful Infographics
Infographics are great tools. They allow rapid dissemination of information without a lot of reading.
When you create infographics on topics relevant to your industry, it can exponentially increase the likelihood that another content marketer sees your graphic and links to it in their next blog post.
Give What You Get
Although we’re talking about inbound linking, we can’t discount the power of outbound linking. By linking out to other members in your industry, you grow your community.
Not only that, but you also increase the likelihood that the goodwill outbound linking will return the favor in the form of inbound linking.
Create Unique Content
Notice missing content about your specific industry? Chances are, you’re not the first to notice content holes.
When you encounter missing content, you should prioritize taking advantage of the hole and filling in the gaps in information.
This strategy not only benefits your site by further establishing you as an expert in the field, but it also creates opportunities for others in your industry to link to your content, earning you even more inbound links.
Aid a Journalist in Need
HARO (Help a Reporter Out) is a service that connects journalists with potential sources. Three times a day, HARO sends emails that share topic areas and specific questions journalists are hoping to be answered, like the one in the image below:

When you share responses to these questions, journalists typically indicate your role as the source, linking back to your site and scoring you additional inbound links.
Create Long-Form Content
If you’re not writing long-form content, tomorrow is the day to start.
Long-form content can gain you more online visibility in the measure of likes and shares, an opportunity to engage more with your community, and serve as a clear indicator of industry expertise.
How does long-form content help you combat Google bias?
A serpIQ study found the best-performing content usually tallied over 2,000 words.
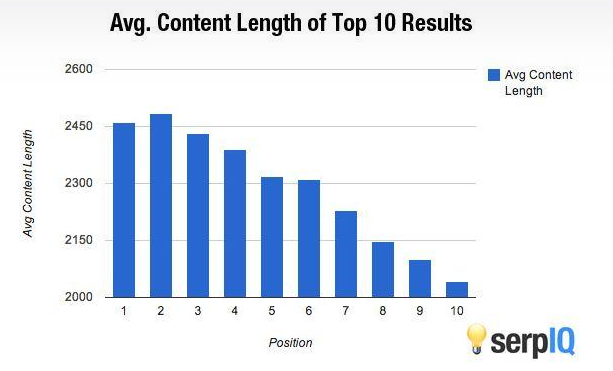
Research conducted by Brian Dean underlines the finding that long-form content is much more valuable to users than its shorter counterpart in many cases.
Now that we know long-form content performs better, how can it eliminate Google bias and help make your site more visible to future consumers?
Below are the top two reasons why long-form content can help your site emerge from the shadows of big brands.
Authority
We talked about the importance of establishing expertise in all content development, and this tenet is nowhere more true than in long-form content.
When you create extensive guides, blog posts, white papers, books, and other deep content dives, you not only establish yourself as an expert among your peers, but you also begin to establish yourself as an expert to search engines.
This can give your content and your site a much greater chance of being seen by an unindoctrinated searcher and overcoming existing Google bias.
SEO
When you create long-form content, you have nearly endless opportunities to use keywords to your advantage.
In shorter content, deploying multiple keywords may present a challenge, but with high word counts come more opportunities for you to make your keywords do as much work as possible.
When you start winning on some of your identified keywords, your site can begin to climb in SERP rankings, making you more visible to searchers, providing an edge over your competitors, and removing existing Google bias.
Conclusion
While it is inarguable that Google bias exists, it’s important to remember Google bias isn’t inherently bad, and it doesn’t mean small businesses are incapable of overcoming search barriers.
By incorporating these elements into your digital strategy, you can begin to surmount Google bias and start increasing your site’s rank on the SERPs.
As you implement these strategies, keep customer intent in mind and remember not to create content for content’s sake. Like most things, when it comes to content strategy, quality prevails over quantity.
Which white hat strategy have you found most effective to use against Google bias?
The post 8 White Hat Strategies for Combating Search Engine Bias appeared first on Neil Patel.